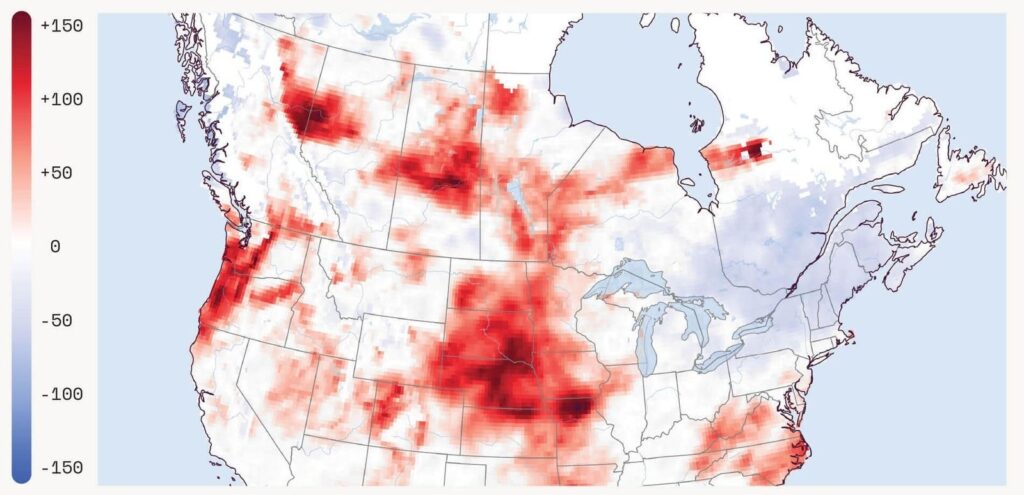
Extreme spring fire risk is rising across North America. Fire Weather Index % Change showing areas … More
Carl Robichaud and Max Dugan-Knight
What happens when the models tell you the world is on fire, and the market listens?
In California’s most extreme wildfire zones, one in five homes has lost its insurance coverage since 2019 according to a recent wildfire research report. In some ZIP codes, premiums have skyrocketed over 40%. More than 150,000 households are now uninsured—not because they want to be, but because they’re uninsurable. And this isn’t a future problem. Wildfire season has barely begun, and already over 200 blazes rage across Canada, many completely out of control. This isn’t just a climate story. It’s a markets story. A systems story. A story of how the first real stress test of climate adaptation is happening—not in the halls of Congress or Parliament, but in your homeowner’s insurance renewal letter.
Insurance Is a Canary in the Climate Coal Mine
Insurers have one job: predict risk, price it, and spread it. And they’re good at it—until they’re not. When Los Angeles was engulfed in flames in January, insurance companies paid out more than $44 billion in claims. State Farm alone lost $7.6 billion. California’s state-subsidized FAIR plan took a $4.8 billion hit. That plan, by the way, is supposed to be the insurer of last resort. It’s now the only option left for hundreds of thousands of homeowners—and it’s buckling.
Insurers saw it coming. Their catastrophe models—backed by more granular data and better forecasting than most public agencies can afford—warned them. They raised premiums, cut policies, and eventually fled entire markets. Since 2018, over 30,000 households in California’s high-risk fire zones have had their policies simply not renewed. Many never got a replacement.
This isn’t a tale of irrational panic. It’s a rational response to a mathematically unsustainable situation. You can’t underwrite homes in areas where the probability of destruction is not only high—but increasing. You can’t make the numbers work when wildfire seasons are longer, fires more intense, and the climate system more volatile.
A Vicious Market Spiral
It gets worse. Homeowners who lose private insurance are turning to FAIR plans—state-backed programs originally designed as temporary backstops. In California alone, enrolment has more than doubled since 2020. FAIR plans offer less coverage, higher deductibles, and few protections for personal property. They’re expensive, incomplete, and dangerously overstretched. But they’re all that’s left.
And because FAIR plans are funded by assessments on private insurers, every loss they take feeds back into the same system that’s already retreating. It’s a vicious cycle: more risk, more exits, more burden on the few insurers who remain, which leads to… more exits.
Add in one more ingredient: population growth. Incredibly, the number of people moving into high-risk areas is growing faster than those leaving. The share of uninsured households is rising even as more homes are being built in harm’s way.
Real Estate Meets Climate Reality
The implications for housing markets are profound. Without insurance, homes can’t get mortgages. Without mortgages, property values collapse. And when homes burn without coverage—as many will—someone pays. Usually, taxpayers. Governments will step in to purchase destroyed properties or prevent rebuilding in zones now understood as climate sacrifice zones.
What we’re witnessing is the first collapse of a financial market under the weight of climate risk. Not in theory. In real time.
The story in California is now echoing across the continent. FAIR plan enrolments are up 54% in Texas and 39% in Oregon. In the U.S. Southwest, drought has pushed fire risk to ten-year highs across Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. In Mexico and Canada, spring fire risk is breaking records. Manitoba has already declared a state of emergency as two people have died, with thousands more evacuated. And it’s only June.
Behind it all is a term climate scientists now use with chilling precision: hydroclimate whiplash. It’s a swinging pendulum weather phenomenon of too-much-then-too-little water. Years of heavy rainfall grow dense vegetation. A sudden drought turns that growth into kindling. Add record temperatures, early snowmelt, and wind—and the landscape becomes a fuse waiting for a spark.
The data backs it up. Fire Weather Index anomalies across North America show levels of risk unseen in over a decade. More fires will come. More homes will burn. More markets will break.
The Feedback Loop No One Budgeted For
Here’s the deeper problem: fires don’t just destroy property, they also emit carbon into the atmosphere. In 2023, Canadian wildfires released more carbon than oil & gas, transportation, buildings, or heavy industry. That carbon accelerates climate change. Which raises temperatures. Which increases drought. Which drives more fires. Which, yes, releases more carbon. That’s the feedback loop we’ve entered.
And yet, our policies remain reactive, not preventative. Our markets—home insurance, housing, municipal bonds—are starting to price climate risk faster than our politics can respond.
We used to think climate change would hit slowly. But wildfire insurance isn’t disappearing slowly. It’s collapsing now. And it’s showing us a hard truth: markets can adapt faster than governments—but not without consequences. When markets exit, people get left behind.
What the wildfire crisis reveals is not just the cost of climate change—but the cost of delay. The systems we rely on—insurance, housing, public finance—weren’t built for this. And they’re beginning to fail. What comes next will depend on whether we treat this collapse as a warning, or as a preview.
Disclaimer: I work for Deep Sky, a carbon removals project developer.